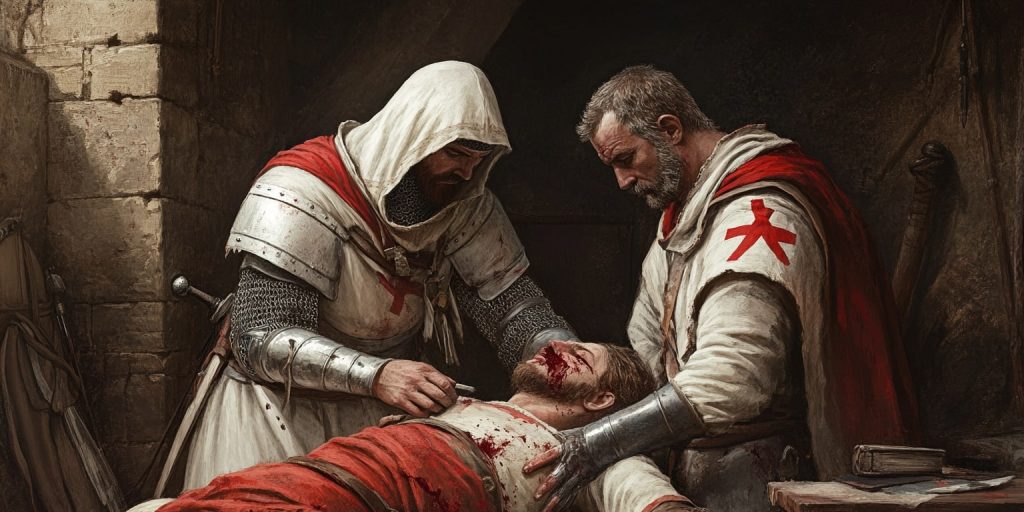
The Crusades were a time of war and medical practice in medieval Europe. Templar Knights fought battles and got hurt, requiring the expertise of apothecaries and medical practitioners. They needed healers to help them.
Medieval healers used their medical knowledge to treat injuries and diseases effectively. They worked hard to keep the Knights safe and healthy, which shows how important medical quality primary care was during the Crusades.
The Role of Templar Knights in the Crusades
The Templar Knights were a key military group in the Crusades, showcasing the importance of military strategy in the medieval period. These events happened from the late 11th to the late 13th centuries, marking significant changes in medical knowledge. They were founded in 1119 to protect Christian pilgrims going to the Holy Land, where they could practice medicine.
Soon, their mission grew in the context of the history of medicine. They got involved in battles to take back Jerusalem and other important places from Muslims, influencing the practice of medicine.
The Templar Knights were known for their great fighting skills. They were famous for their strong formations in battle. They fought big battles like the Battle of Hattin and the Siege of Acre.
They helped win these battles, showing their bravery and faith. The Templars also helped by providing food, supplies, and strategy to other fighters.
- Templar Knights were key in keeping pilgrims safe.
- They had a lot of money and resources, helping them stay strong in the Holy Land.
- They built strong forts to help protect the Crusaders and maintain their strategic advantage during the medieval period.
Many knights were injured in battle, which showed the need for better healing. The Templars helped start early medical care.
This care was the first step towards better medicine in war, laying the groundwork for later medieval advancements. Their care for each other showed their strength and the value of medicine in fighting during the medieval period.
Understanding Medieval Medicine During the Crusades
Medieval medicine during the Crusades mixed superstition, religion, and new scientific ideas. Soldiers used what they knew from early medieval medicine to heal battle wounds. They believed in the humoral theory, which said illness came from body fluid imbalances, a concept in many medical texts.
Churches were key in medical care back then. Monasteries were places where people could get medical help. They believed that God’s help was needed to get better.
Doctors used old texts to guide them but knew little about the body. They used herbs and natural remedies to help. Surgery was not well understood and was very dangerous.
Doctors tried different things to see what worked. This way of learning helped start new medical ideas. So, medieval medicine was a mix of old ways, faith, and trying new things.
Medieval Healers: Their Education and Knowledge
Medieval healers learned much from ancient doctors and manuscripts that detailed early medical practices. Hippocrates and Galen were key figures, and their teachings shaped how medicine was practiced in the Middle Ages.
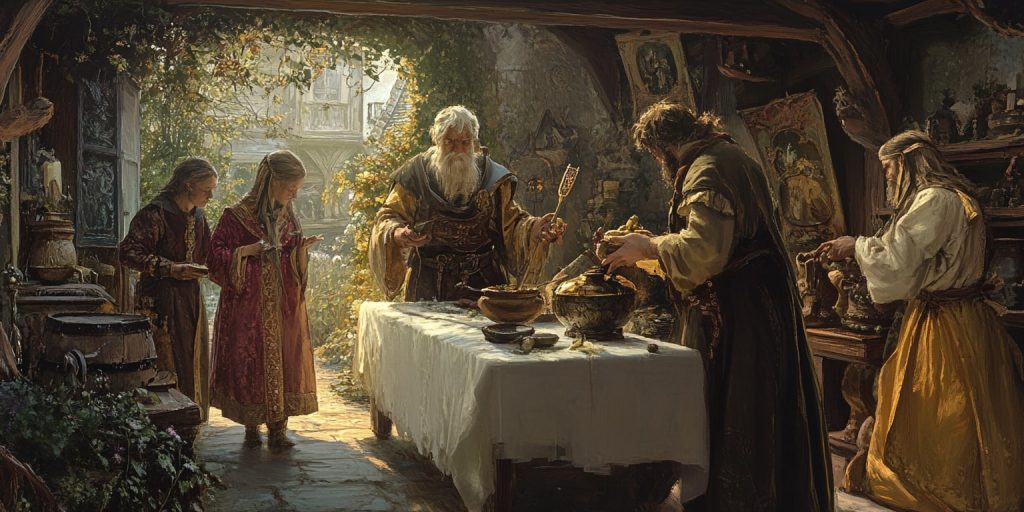

Influence of Ancient Texts: Hippocrates and Galen
Hippocrates, known as the “Father of Medicine,” focused on observing and treating patients. He believed in treating the whole person, not just symptoms. Galen, a Roman doctor, built on Hippocrates’ ideas. He stressed the importance of knowing the body’s anatomy and the four humors, which were foundational to the practice of medicine.
These teachings were key in medieval medicine. They helped shape how doctors were trained for centuries.
Medical Schools: Salerno and Montpellier
Salerno and Montpellier were the top medical schools in the Middle Ages. Salerno was known for its advanced learning and as a center for medical texts in medieval Europe. It focused on understanding ancient texts.
Montpellier was famous for its tough training and high standards. Students who went there became skilled doctors, contributing to the evolving practice of medicine. They knew a lot about ancient medicine and how to apply it.
Common Healing Practices Employed for Warriors
Medieval medicine used natural remedies and techniques to help warriors. Healers, including barbers, used many ways to help them heal and feel better, showcasing the diverse practice of medicine. This includes herbal remedies and surgical methods like bloodletting.
Herbal Remedies and Natural Cures
Herbal remedies were key in medieval medicine. Healers used plants for their healing powers. Some common ones were:
- Willow bark: Known for its pain-relieving qualities.
- Chamomile: Used for its soothing properties and to promote sleep.
- St. John’s Wort: Employed for wound healing and as an anti-inflammatory, these practices were part of the medical knowledge of the era, documented in various manuscripts.
- Garlic: Recognized for its antibacterial properties and ability to prevent infections, this knowledge was crucial in early medieval medicine.
These natural cures were made into infusions, poultices, or ointments. This shows how clever medieval healers were in their practices and knowledge of medicine in the Middle Ages.
Surgical Techniques and Bloodletting
Surgical techniques improved a lot during this time. They focused on treating injuries from battle, a significant aspect of early medieval medicine. Practices included cleaning wounds, stitching, and using antiseptic herbs.
Bloodletting was also common. It was believed to balance the body’s humors. This involved draining blood to treat ailments. Though we see it differently today, the medical knowledge of that time, especially in the context of medicine in the Middle Ages, was important back then.
Herbal remedies and surgical techniques were both crucial. They helped warriors during the Crusades, reflecting the vital role of medical practitioners in the medieval period. Both were important in a time of many health challenges and limited resources.
Spiritual Healing and the Care of the Sick
Spiritual healing and medical care were closely linked in medieval times. Monasteries and religious orders were key to this connection. They offered a safe place and treatment for the sick.
These places didn’t just treat physical ailments. They also helped with emotional and spiritual needs. The healers of that time believed in the power of faith in their work.
The Role of Monasteries and Religious Orders
Monasteries were important for healing back then. They were run by monks and nuns who knew a lot about healing. They used herbs and spiritual care to help the sick.
Thanks to religious orders, people got both medical and spiritual help. This mix of techniques made healing in medieval times more effective in medicine.
Spiritual Practices in Healing
Spiritual healing was a big part of recovery in medieval times. People used prayer and rituals and asked for divine help, believing these practices made treatments work better.
This shows how medieval healers saw health as a whole. They believed in treating the body, mind, and spirit together.
Women Healers in Medieval Medicine
Women were key in medieval medicine, often being the main caregivers. They were known as wise women, using herbal medicine to treat many illnesses. Their skills were highly valued; they were the first to help those in need.
They kept important health knowledge alive, helping many people stay healthy.
Wise Women and Their Role in Communities
Wise women were vital in medieval societies, playing a big role in healthcare. They used local herbs to help the sick, and people trusted them a lot, especially when they were ill.
They built a strong support network, helping with both physical and emotional health.
Herbal Medicine and Midwives
Midwives were also very important, focusing on women’s health and childbirth. They used herbal medicine to support mothers during labor and helped with other health issues.
Together, women healers, such as wise women and midwives, shaped medieval medicine. They ensured that quality primary care was available and effective in their communities.

