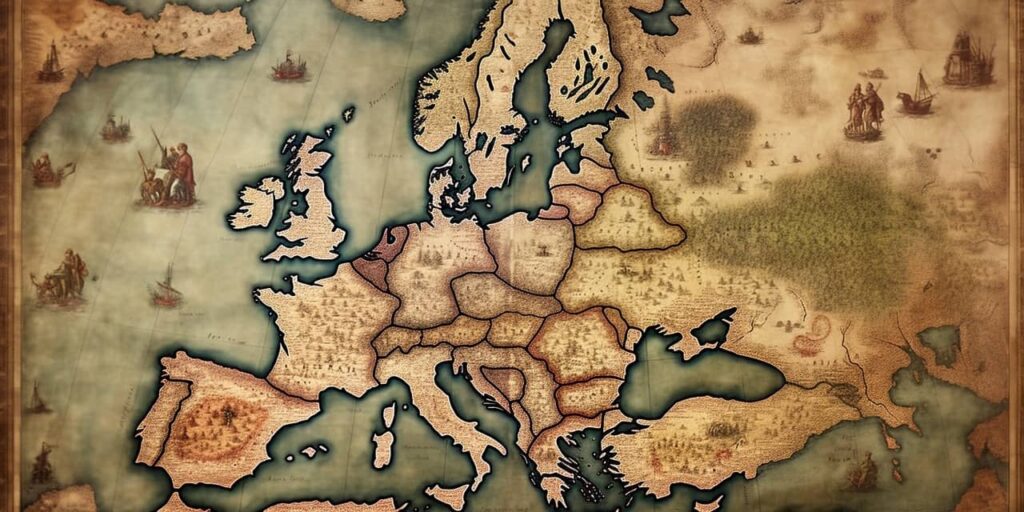
Travel back in time and immerse yourself in the captivating world of the medieval map of Europe. These historical maps offer a glimpse into the rich history and culture of Europe during the Middle Ages. From the intricate details to the historical significance, exploring these maps provides valuable insights into bygone eras.
In this section, we will delve deep into the medieval map of Europe, focusing on its historical significance and intricate details. Join us on a journey through time and uncover fascinating insights from this bygone era.
Key Takeaways
- Medieval maps of Europe are a valuable tool in understanding the history and culture of Europe during the Middle Ages.
- Exploring the intricate details of these maps allows us to appreciate the artistry and knowledge that went into their creation.
- These historical maps offer insights into the geography, boundaries, and regions of Europe during the medieval period.
- Understanding the evolution of European cartography during this time is essential in comprehending the development and advancement of mapping techniques.
The Evolution of European Cartography
During the medieval period, European cartography underwent a significant transformation. Prior to this era, maps were largely symbolic representations of the world, lacking precise details or accurate measurements. However, as trade and exploration expanded across Europe, the need for more accurate maps became increasingly necessary.
The earliest medieval maps of Europe were drawn on parchment or vellum and were highly detailed. They included information on topography, climate, and natural resources. The maps were created using a variety of techniques, including triangulation, compasses, and celestial navigation.
One of the most significant advancements in European cartography during the medieval period was the development of portolan charts. These navigational maps used detailed coastal information and allowed sailors to chart courses more accurately than ever before. As a result, trade and exploration flourished, and European cartography continued to evolve.
The Evolution of European Cartography
During the medieval period, European cartography underwent a significant transformation. Prior to this era, maps were largely symbolic representations of the world, lacking precise details or accurate measurements. However, as trade and exploration expanded across Europe, the need for more accurate maps became increasingly necessary.
The earliest medieval maps of Europe were drawn on parchment or vellum and were highly detailed. They included information on topography, climate, and natural resources. The maps were created using a variety of techniques, including triangulation, compasses, and celestial navigation.
One of the most significant advancements in European cartography during the medieval period was the development of portolan charts. These navigational maps used detailed coastal information and allowed sailors to chart courses more accurately than ever before. As a result, trade and exploration flourished, and European cartography continued to evolve.
Uncovering Ancient Europe through Maps
The medieval map of Europe provides valuable insights into the geography, boundaries, and regions of ancient Europe. These maps are a treasure trove of information for historians, cartographers, and enthusiasts alike.
By studying the medieval maps of Europe, historians have been able to unearth hidden information about ancient Europe. These maps provide us with a snapshot of the past, revealing the changing political and cultural landscapes of this bygone era. They allow us to examine how the territories of different empires changed over time, and how they interacted with each other.
Through the medieval maps of Europe, we can also gain insights into the lives and culture of the people who inhabited these regions. The maps depict the various cities, towns, and landmarks of Europe, giving us a glimpse into the daily lives of people during the medieval period. We can also learn about the trade routes, migration patterns, and cultural exchanges that took place throughout Europe.
The medieval maps of Europe were not just practical tools for navigation and exploration, they were works of art. The intricate details and ornate decorations on these maps reflect the artistic styles and cultural traditions of the time. They were often commissioned by wealthy patrons and monarchs who sought to showcase their power and influence through these maps.
Today, the study of medieval maps of Europe continues to provide valuable insights into our shared history. By preserving and analyzing these ancient artifacts, we can deepen our understanding of the world that came before us and appreciate the artistry and skill that went into their creation.
Exploring the Geography of Medieval Europe
The medieval maps of Europe were not just pieces of art but also valuable sources of geographical information. These maps provide us with an insight into the landscape, regions, rivers, mountains, and their respective boundaries. The depiction of various topographical characteristics of Europe was an essential part of the medieval mapmaking- a skill that was perfected over the years.
Medieval European cartographers used different techniques to represent the geography of Europe. They employed symbols, colors, and shading techniques to portray the depth, height, and curvature of landforms. For instance, green color often represented plains, yellow depicted hills, and brown represented mountains. These techniques allowed cartographers to create visually appealing maps while providing an accurate representation of geography.
Maps of medieval Europe were comprehensive, depicting the vastness of the continent and the intricate details of its geography. For example, the maps showed the Alps, the Pyrenees, and the Carpathians Mountain ranges, the rivers Danube, Rhine, and Vistula, among others. The depictions of the geography of Europe allowed medieval travelers and explorers to navigate and understand the continent’s terrain more efficiently.
Mapping the Medieval Kingdoms
Medieval maps of Europe provide us with a detailed picture of the political divisions during that era. From the Frankish Empire to the Byzantine Empire, medieval cartographers depicted the kingdoms and territories of the time. These maps were not only a representation of the physical world but also the political landscape of Europe.
Mapping the Borders and Territories
Medieval maps of Europe were created during a period where political borders were constantly shifting. This meant that cartographers had to update their maps regularly to reflect the current territories and borders. The maps depicted the various kingdoms, principalities, and regions of Europe, often with detailed illustrations of castles and other significant landmarks. The borders of these territories were marked by dotted lines, often with the name of the ruler or kingdom written next to it.
Political Divisions on the Map
Medieval maps of Europe not only showed the physical geography but also the political divisions of the time. They depicted the various political entities, such as kingdoms, duchies, and principalities, that existed during the medieval period. The maps also included detailed illustrations of the capitals and other major cities of each kingdom. These maps were not only useful for navigation but also for understanding the political landscape of Europe during that time.
The Artistry of the Medieval Map of Europe
The maps produced during the medieval period were not only functional but also works of art. The cartographers of the time were skilled in creating beautiful and intricate maps. They used a range of techniques, such as coloring and shading, to make the maps more visually appealing. The maps often included illustrations of sea monsters, mythical creatures, and other decorative elements that added to their appeal. These maps are considered to be some of the most beautiful examples of cartography in history.
Overall, medieval maps of Europe offer a fascinating insight into the political landscape of the time. With their attention to detail and artistic style, these maps are not only informative but also visually stunning. Revealing the kingdoms and territories of medieval Europe, exploring these historical maps is an adventure in itself.
The Intricacies of Medieval Map Symbols
One of the most fascinating aspects of medieval maps of Europe is the intricate symbols and legends used to depict geographical features and landmarks.
These antique maps are adorned with a wide array of symbols, ranging from religious icons to mythological creatures. Some of the most commonly used symbols include lions, eagles, dragons, and unicorns.
These symbols were not just decorative features; they served a functional purpose as well. Many of these symbols were used to denote political boundaries or important cities, while others were used to represent different landforms such as rivers, mountains, or forests.
Another interesting aspect of these vintage European maps is the use of colors. Each color was specifically chosen to represent different regions or kingdoms, and would often be accompanied by a symbol or emblem unique to that region.
The study of these intricate symbols and legends has shed light on the artistic talent and technical skill of medieval cartographers. It is evident that the creation of these maps required a great deal of expertise, as well as a deep understanding of geography and history.
Examples of Medieval Map Symbols
| Symbol | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Castle | Important city or fortress |
| Cross | Religious site or landmark |
| Mermaid | Maritime location or sea monster |
| Tree | Forest or woodland area |
Overall, the intricate symbols and legends used in medieval maps provide a unique glimpse into the worldview and cultural beliefs of this bygone era. These antique maps allow us to explore not just the geography of Europe in the Middle Ages, but also the artistic and technical achievements of the people who created them.
Navigating the Seas on Medieval Maps
Medieval maps of Europe were not limited to the depiction of land masses and kingdoms. They also included detailed information about the seas and oceans surrounding Europe. These historical maps were considerably more advanced in terms of oceanic navigation than previously thought.
One intriguing example is the depiction of sea monsters, which served as both warnings to sailors and decorative elements of the maps. Medieval cartographers also included navigational information, such as wind directions, currents, and important ports of call along maritime routes.
Despite some inaccuracies, medieval maps were fairly reliable in terms of their depiction of coastlines, islands, and major bodies of water. This is because cartographers would often consult with sailors and other seafarers, who provided firsthand knowledge of the seas and oceans they traversed.
Overall, the maritime information depicted on medieval maps offers a fascinating glimpse into the navigational techniques of the era. These maps provide a unique insight into the dangers and wonders of the world that medieval sailors navigated.
The Influence of Religion on Medieval Maps
The medieval map of Europe was heavily influenced by religion, as Christianity played a dominant role in medieval European society. As a result, many of the medieval maps included religious landmarks and pilgrimage routes, as well as depictions of events from the Bible.
The maps were often used as a tool for teaching religious history and geography. For example, the mappa mundi, a type of medieval map that was used to illustrate the history of the world in terms of biblical events, often included imagery such as Adam and Eve in the Garden of Eden, Noah’s Ark, and the crucifixion of Jesus.
Religious landmarks were also prominent on the maps, such as the depiction of Jerusalem and other holy sites. Pilgrimage routes were often included as well, such as the popular pilgrimage to Santiago de Compostela in Spain, which was a popular destination for medieval Christians.
The influence of religion on medieval maps extended beyond just landmarks and routes, as the maps also reflected the religious beliefs of the time. For example, some maps depicted the Earth as flat, with Jerusalem at the center, as this was consistent with the Christian belief that the city was the spiritual center of the world.
Overall, religion played a major role in shaping the content and imagery of medieval maps of Europe. By studying these maps, we can gain valuable insights into the religious beliefs and practices that shaped medieval European society.
Preserving and Analyzing Medieval Maps Today
The medieval map of Europe offers a unique insight into the past, reflecting the artistic and cartographic skills of the time. These antique maps represent a valuable source of information for historians, geographers, and art enthusiasts alike. As such, efforts are made to preserve and analyze these delicate artifacts both for their historical significance and their beauty.
Due to their age and fragility, it is essential to protect medieval maps from damage caused by light, humidity, and other environmental factors. Institutions such as museums, libraries, and universities that possess these antique maps invest in specialized storage and display solutions to ensure their longevity.
Alongside preservation efforts, medieval maps undergo analysis to reveal new insights into the times they depict. Through advanced imaging techniques, scholars can uncover hidden details and better understand the processes used to create medieval maps of Europe. By studying the symbols, the geography, and the artwork found on these maps, experts gain valuable insights into the past.
Today, antique maps are actively used in research, education, and exhibitions. They serve as primary sources for historical information, as well as cultural and artistic artifacts. The study of medieval maps of Europe enables us to deepen our understanding of the past and appreciate the skill and sophistication of those who created them.
Conclusion
Exploring the medieval map of Europe is an incredibly enriching experience. From the historical significance it holds to the intricate details it contains, these maps offer a glimpse into a bygone age of cartography and storytelling.
Through studying these maps, we gain a deeper understanding of the evolution of European cartography and the advancements made in mapping techniques during the medieval period. We also uncover valuable insights into ancient Europe, its geography, boundaries, and regions.
One notable feature of medieval maps is their depiction of kingdoms and political divisions. By exploring these boundaries, we can gain a deeper understanding of the medieval power structures and political climate of Europe.
The symbols and legends used in medieval maps are also fascinating to explore. They offer insights into how cartographers represented various geographical features and landmarks, allowing us to navigate and understand the maps better.
Furthermore, the preservation and analysis of medieval maps in the present day are incredibly important. These ancient artifacts give us clues about the past and help us better understand the history of Europe.
In conclusion, the medieval map of Europe offers a rich and captivating history. Exploring these maps and their intricate details is an adventure in itself, providing valuable insights into the evolution of cartography, the geography of Europe, and the rich history of medieval kingdoms.
FAQ
Q: What is the significance of medieval maps of Europe?
A: Medieval maps of Europe provide valuable insights into the geography, boundaries, and regions of Europe during the medieval period. They offer a glimpse into the political divisions, kingdoms, and cultural practices of the time.
Q: How were medieval maps of Europe created?
A: Medieval maps of Europe were created through careful observation, measurements, and explorations. Cartographers used a combination of artistic skill and scientific knowledge to depict the geography and landmarks of the continent.
Q: What symbols and legends were used in medieval maps?
A: Medieval maps of Europe featured intricate symbols and legends to represent various geographical features and landmarks. These symbols could range from mountains and rivers to religious sites and trade routes.
Q: How did religion influence medieval maps of Europe?
A: Religion played a significant role in shaping the depiction of medieval maps. Important religious landmarks, pilgrimage routes, and religious sites were often prominently featured, reflecting the cultural and spiritual significance of these locations.
Q: How do we preserve and analyze medieval maps today?
A: Efforts are made to protect and study medieval maps to ensure their preservation. Various techniques, including digital imaging and conservation practices, are employed. These maps are analyzed to gain insights into European history and the techniques used by medieval cartographers.