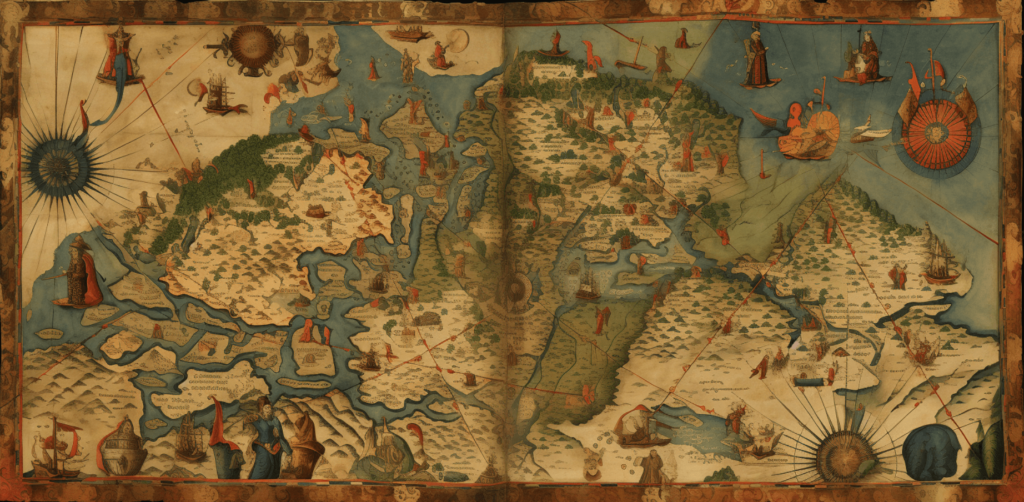
Travel back in time and explore the world of medieval maps. These ancient cartographic wonders provide valuable insights into historical landscapes and offer a glimpse into the complex world of navigation and exploration during the Middle Ages.
Medieval maps are not just simple geographical representations of the world, but they also reflect the social, cultural, and religious ideologies of their time. These maps were created by skilled craftsmen who blended science and art with creativity to produce maps that were not only functional but also beautiful.
Join us on a journey to discover the intricacies of medieval maps and the fascinating stories they tell about the past.
Key Takeaways
- Medieval maps offer valuable insights into historical landscapes.
- These maps reflect the social, cultural, and religious ideologies of their time.
- Medieval maps were created by skilled craftsmen who blended science and art with creativity.
- Medieval maps are not just functional but also beautiful.
- Exploring medieval maps can be a fascinating journey into the past.
Unveiling the Beauty of Medieval Cartography
Medieval maps are more than just navigational aids; they are artistic masterpieces. Cartographers of the Middle Ages blended scientific knowledge with creative flair to produce visual representations of the world that were both functional and aesthetically pleasing.
One of the most striking features of medieval maps is their attention to artistic details. Decorative elements such as elaborate illustrations, embellished borders, and calligraphic fonts were used to enhance the beauty of these maps. These maps were often painted using vibrant colors and intricate patterns, making them pieces of art that were meant to be admired as much as they were used for practical purposes.
The craftsmanship behind these maps is truly remarkable. Cartographers used a range of techniques to create intricate symbols and illustrations, often combining different media such as ink and watercolors. These maps were not only functional but also visually stunning, with each detail and element carefully planned and executed.
At the time, many of these maps were considered expensive and exclusive luxury items, only accessible to the wealthiest and most elite members of society. Today, they continue to captivate and inspire people around the world, appreciated both for their historical significance and their artistic beauty.
Understanding the Purpose of Medieval Maps
Medieval maps were not only works of art, but they served practical purposes as well. Navigation was a primary concern for medieval explorers and merchants, and maps were instrumental in aiding their journeys. These maps were created to provide geographic knowledge of the time, but they were limited by the lack of technology and exploration. As a result, many maps from this era contained inaccuracies, and some regions were depicted based on speculation rather than empirical evidence.
The primary aim of medieval maps was to aid navigation, but they were also created for religious, political, and educational purposes. For instance, they often included symbols and drawings that portrayed religious beliefs and cosmological ideas. These maps were also used to convey political boundaries and regional topography. Scholars also used these maps to educate themselves on geography, history, and literature.
Navigation Techniques
Maps were essential to medieval navigation, and cartographers used various techniques to calculate distances and directional bearings. One such technique was the compass and magnet, which was used to determine direction. Distance was measured using mathematical calculations based on the length of the journey. Using these methods, cartographers could create maps that were accurate enough for practical navigation.
Limitations of Geographic Knowledge
Medieval cartographers faced numerous challenges due to limited exploration and knowledge of the world. As a result, many maps from this era were missing key details, such as the shape and size of continents. Inaccuracies also resulted from cultural biases and a lack of scientific understanding. Nonetheless, these maps offer invaluable insights into the world as it was perceived during the Middle Ages.
Overall, medieval maps were an essential tool for navigation and a valuable representation of geographic knowledge in the past. They offer a unique glimpse into the mindsets and political landscapes of the time. As we continue to study these artifacts, we gain a deeper understanding of our shared history and the evolution of cartography over time.
Types of Medieval Maps
Medieval maps can be broadly categorized into two distinct types; mappa mundi and portolan charts. While both these maps were created with the primary aim of helping people navigate through unknown terrains, they differ significantly when it comes to their design and function.
Mappa Mundi
Literally meaning ‘world map’ in Latin, mappa mundi was a type of medieval map that was created with the aim of representing the world and its various features as they were perceived at the time. Typically, mappa mundi was circular in shape and heavily decorated with illustrations and symbols that represented various religious or historical elements.
| Characteristics of Mappa Mundi | Function |
|---|---|
| Heavily decorated with symbols and illustrations | Representation of the world |
| Religious elements and landmarks depicted prominently | Historical and cultural significance |
The T and O map is one of the most well-known examples of mappa mundi, which represented the world in a T shape, with the three continents known to medieval Europeans: Asia, Europe, and Africa, forming the arms of the cross. Jerusalem was typically placed at the center of the map, while the Garden of Eden was often depicted at the top.
Portolan Charts
Unlike mappa mundi, portolan charts were designed to aid sailors and navigators in their travels. These maps were highly detailed and accurate, with coastlines and ports marked out precisely. They were typically created on parchment made from animal skin and used as navigational material by sailors.
| Characteristics of Portolan Charts | Function |
|---|---|
| Highly detailed and accurate | Navigational tool for sailors and travelers |
| Marked with coastlines, ports, and sailing routes | Used to navigate through unknown seas |
The Portolan Atlas, created by Italian cartographer Pietro Vesconte in the early 14th century, is one of the most impressive examples of portolan charts. It was widely used by sailors across the Mediterranean and Black Sea regions.
Both mappa mundi and portolan charts offer unique insights into the medieval world and continue to fascinate historians and map enthusiasts to this day.
Decoding the Symbols and Legends on Medieval Maps
Medieval maps are not only known for their stunning illustrations but also for the numerous symbols and legends that adorn them. These markings were used to represent various geographical features, cultural landmarks, and mythical creatures.
Understanding the meaning behind these symbols and legends is crucial for interpreting a medieval map’s content accurately. Many cartographers of the Middle Ages included a key or legend within the map to help viewers decipher the map’s symbols and references.
| Symbol/Legend | Meaning |
|---|---|
| The Compass Rose | A symbol indicating the four cardinal directions (north, south, east, and west) and their intermediate points. It helps viewers orient themselves with respect to the map. |
| The Ship | Indicates maritime travel and navigation, often accompanied by symbols for sea monsters and other dangers. |
| The Dragon | A mythical creature representing unexplored territories or areas believed to be inhabited by dangerous beasts. |
| The City or Castle | Represents a significant cultural or political center, often marked with a symbol for a church or other religious building. |
| The Tree | A symbol used to mark the location of a forest or wooded area. |
Other symbols commonly found on medieval maps include mountains, rivers, animals, and religious icons. The use of these symbols reflects a blend of cartographic skill and cultural beliefs and customs.
Deciphering the symbols and legends on a medieval map is not always straightforward. Cartographers of the past often used personal, cultural, or religious references that may be difficult for a modern audience to understand. However, with careful examination and research, these maps can provide a fascinating insight into the beliefs and knowledge of past civilizations.
Mapping the Medieval World: Landscapes and Territories
Medieval maps offer a fascinating look into the known world of the time and how it was conceptualized by cartographers. These maps often depicted landscapes and territories with great detail and artistic flair.
One of the most striking features of medieval maps is the way landscapes are represented. Mountains, rivers, and forests were common motifs, and were often illustrated in great detail to give the viewer a sense of the region’s topography. Cartographers also used symbolic representations to convey information about the land, such as representing trees with clusters of leaves to indicate a wooded area, or using waves to depict a body of water.
Another important aspect of medieval maps was the depiction of territories. Political boundaries were often marked with bold lines, and sometimes included flags or other symbols to denote ownership or allegiance. Cities and towns were frequently depicted with miniature illustrations, offering a glimpse into the built environment of the time.
Mapping the Cosmos:
In addition to depicting physical landscapes, medieval maps often contained cosmological representations as well. These map types, called mappa mundi, were world maps that combined geographic information with religious and mythological symbolism. While they were not intended for navigation, these maps offer valuable insights into the medieval worldview and how it was shaped by various cultural beliefs.
Overall, medieval maps offer a rich and complex view of the world as it was understood during that time period. They offer a unique perspective into the past and the cultural, political, and religious forces that shaped it.
Challenges and Limitations of Medieval Mapmaking
Medieval cartographers faced numerous challenges and limitations in their quest to create accurate maps. The limitations imposed by the lack of technology, limited exploration, and cultural biases affected the accuracy and scope of medieval maps.
The lack of sophisticated measuring tools and navigational instruments during the Middle Ages made it difficult for cartographers to produce accurate depictions of the world. As a result, medieval maps often featured distorted shapes and sizes of continents and countries.
Another challenge was the limited geographical knowledge of the time. Many regions of the world were either unknown or poorly understood, which made it difficult for cartographers to create accurate maps.
Cultural biases also played a significant role in shaping medieval maps. Religious and political beliefs often influenced the portrayal of certain regions and countries, leading to the inclusion or exclusion of specific features or landmarks.
Despite these limitations and challenges, medieval cartographers continued to produce maps that captured the spirit of exploration and discovery. Their maps may not have been wholly accurate, but they remain valuable artifacts that provide an intriguing glimpse into the world as it once was.
Preservation and Rediscovery of Medieval Maps
The preservation and rediscovery of medieval maps have been a crucial aspect of ensuring that these valuable artifacts are accessible to the present and future generations. Throughout history, many medieval maps were lost or destroyed due to wars, natural disasters, and neglect. However, the efforts of scholars, collectors, and institutions have played a vital role in preserving and restoring these precious documents.
One of the earliest known attempts to preserve medieval maps was made in the 11th century by the Byzantine princess Anna Komnene. She compiled a comprehensive anthology of ancient cartographic works that included some of the earliest surviving maps.
During the Renaissance period, many European scholars became interested in classical and medieval cartography, leading to the rediscovery of many forgotten maps. One such example is the 6th-century Ravenna Cosmography, which was rediscovered in the 15th century and found to contain valuable information about the ancient world.
In the modern era, the importance of preserving medieval maps has only increased. Many institutions, such as the British Library and the Vatican Library, have dedicated themselves to the conservation and digitization of these maps. This has made it possible for people worldwide to access and study these remarkable artifacts without physically visiting the institutions.
However, the preservation of medieval maps is not without its challenges. The delicate nature of these documents, their age, and often their large size makes them vulnerable to damage and deterioration. Preservationists must use specialized techniques and equipment to protect these maps from light, heat, humidity, and pests. Moreover, the process of digitization requires careful handling and high-resolution scanning to ensure that the maps are fully readable and usable for research.
Nevertheless, the efforts of preservationists and the passion of collectors have made it possible for medieval maps to remain relevant and accessible. Through their work, medieval maps continue to inspire new generations and expand our knowledge and appreciation of the past.
Modern Applications and Appreciation of Medieval Maps
Despite their origin in the Middle Ages, medieval maps continue to captivate and inspire people worldwide. Today, these cartographic treasures find modern-day applications in fields such as archaeology, history, and geography.
Researchers use these maps to gain insights into the historical landscapes, political boundaries, and geographic knowledge of the past. With the advancement of technology, these maps can be digitized, analyzed, and compared with modern maps to understand changes in the landscape over time.
Artists and designers also find inspiration in the intricate details and decorative features of medieval maps. From intricate illustrations to elaborate borders, these maps offer a wealth of design elements that can be used in modern-day projects.
But perhaps the most significant value of medieval maps is their ability to spark curiosity and appreciation for history. These maps provide a tangible link to the past and offer a glimpse into the world as it once was. Their beauty, complexity, and historical significance continue to awe and inspire people of all ages.
Applying Medieval Maps in Education
Medieval maps also have significant applications in education. Teachers can use these maps as educational tools to help students understand historical geography, navigation techniques, and cultural beliefs of the past. These maps provide a unique learning experience that goes beyond traditional textbooks and lectures and offers a hands-on approach to history.
Furthermore, medieval maps can help students develop critical thinking skills through the interpretation of symbols and legends. Students can analyze the underlying meanings of these markings and learn how cultural biases and beliefs of the past influenced mapmaking.
The Appreciation of Medieval Maps as Art
Medieval maps are not just historical relics but also works of art. Their intricate details, elaborate illustrations, and decorative elements make them masterpieces of craftsmanship and creativity. Collectors and enthusiasts appreciate these maps for their artistic value and historical significance.
But collecting medieval maps is not just a hobby for the elite; it is also an opportunity for individuals to own a piece of history. These maps offer a tangible connection to the past and provide a glimpse into the world as it once was.
Whether used for academic research, artistic inspiration, or personal enjoyment, medieval maps continue to fascinate and captivate people worldwide. Their legacy endures as a testament to the ingenuity and creativity of medieval cartographers and the enduring value of historical artifacts.
Collecting and Owning a Piece of History: Medieval Maps for Sale
If you’re a history enthusiast or a collector of rare artifacts, owning a medieval map is a dream come true. These intricate cartographic wonders offer a glimpse into the past and provide valuable insights into the world as it once was. With a growing interest in antique maps, there is a vast market for medieval maps today, where collectors can find authentic pieces of history.
Before purchasing a medieval map, it’s essential to understand its historical significance and authenticity. Due to their age and rarity, these maps require careful authentication and preservation to prevent damage and ensure their accuracy. Before buying a map, it’s essential to work with reputable dealers or auction houses to ensure you’re getting an authentic piece.
Collecting medieval maps is a rewarding hobby that offers an opportunity to immerse oneself in history and art. Each map is a unique representation of the world as it once was, complete with its own cultural biases and artistic style. Collectors can explore the many different types of medieval maps, including mappa mundi and portolan charts, and appreciate the intricate details and artwork that make these maps true works of art.
Whether you’re interested in displaying a medieval map in your home or adding to your collection, there are many options to consider. Some collectors prefer to purchase maps that are in good condition, while others enjoy the challenge of restoring damaged maps to their former glory. The market for medieval maps is continually evolving, and collectors can find unique and rare pieces online and offline.
Owning a medieval map is not only a way to connect with history but also a way to invest in a piece of art that has proven to hold its value over time. These maps are more than just decorative pieces; they are a tangible link to the past and a testament to the ingenuity of the cartographers who created them.
In conclusion, collecting medieval maps is a fascinating hobby that offers a unique connection to the past. If you’re interested in owning a piece of history, take the time to research and understand the significance of each map, and work with reputable dealers or auction houses to ensure you’re getting an authentic piece. With careful preservation and appreciation, a medieval map can be a cherished possession that provides insights and enjoyment for generations.
Unleash Your Inner Historian with a Medieval Map
If you’re a history buff looking for a new way to explore the past, look no further than medieval maps. These cartographic marvels offer an intimate glimpse into the world as it once was, inviting you to explore historical landscapes and territories with rich artistic details and symbolic representations.
The Beauty of Exploration
Embark on a journey back in time and discover the intricacies of a medieval map. Unveil the hidden details and elaborate illustrations that make these maps true works of art. Understand the cartographer’s blend of science and creativity in their efforts to create visual representations of the world.
The Significance of History
Medieval maps have played an essential role in navigation, exploration, and cultural exchange. They offer insights into the historical context of the time and the people who created them. By exploring a medieval map, you can gain a deeper appreciation for the world’s geography, cartography, and cultural history.
The Joy of Collecting
Collecting medieval maps can be a thrilling experience, providing a connection to the past that few other artifacts can offer. These maps offer unique insights into historical landscapes and territories, inviting you to explore the past with a fresh perspective. Whether you’re a seasoned collector or new to the world of medieval maps, owning one of these cartographic treasures can be a rewarding and enlightening experience.
So, what are you waiting for? Unleash your inner historian today and explore the fascinating world of medieval maps. Let these intricate cartographic wonders ignite your curiosity for the past and offer a glimpse into the world as it once was.
FAQ
Q: What are medieval maps?
A: Medieval maps are cartographic representations created during the Middle Ages, typically between the 5th and 15th centuries. They provide insights into historical landscapes and offer a visual depiction of the world as it was understood during that time.
Q: What makes medieval maps unique?
A: Medieval maps are known for their intricate details and artistic elements. They often feature elaborate illustrations, decorative borders, and religious symbolism, showcasing the blend of creativity and scientific knowledge of the cartographers from that era.
Q: What was the purpose of medieval maps?
A: Medieval maps served various purposes, including aiding navigation, facilitating trade and exploration, and providing a visual representation of geographical knowledge at the time. They were essential tools for travelers, merchants, and explorers during the Middle Ages.
Q: What are some types of medieval maps?
A: There were various types of medieval maps, including mappa mundi, which depicted the world as a whole, and portolan charts, which focused on maritime navigation along coastal regions. Each map type had its unique characteristics and purposes.
Q: How were symbols and legends used in medieval maps?
A: Symbols and legends on medieval maps were used to represent geographical features, cultural landmarks, and mythical creatures. They added depth and meaning to the maps and allowed cartographers to convey information about the world in a visual and symbolic manner.
Q: What were the challenges of creating medieval maps?
A: Medieval cartographers faced challenges such as limited technological advancements, limited exploration and accurate geographical knowledge, and cultural biases. These limitations influenced the accuracy and completeness of the maps created during that time.
Q: How were medieval maps preserved and rediscovered?
A: Throughout history, efforts have been made to preserve and rediscover medieval maps. Institutions and individuals dedicated themselves to the conservation and study of these artifacts, ensuring their survival for future generations to appreciate and learn from.
Q: How are medieval maps used today?
A: Medieval maps are still used today for academic research, artistic inspiration, and historical exploration. They offer valuable insights into the past and continue to captivate and educate people worldwide with their enduring significance.
Q: Is it possible to own a medieval map?
A: Yes, it is possible to own a medieval map, although they are rare and unique artifacts. Collecting medieval maps involves understanding the market, the authentication process, and the joy of owning a piece of history.
Q: How can a medieval map unleash your inner historian?
A: By exploring historical landscapes through the lens of a medieval map, you can embark on a journey through time and ignite your curiosity for history. These maps offer a captivating glimpse into the past and provide valuable insights into the world as it once was.